On-line exercises:
Thursday 30 May 2019
Wednesday 22 May 2019
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives and Adverbs
In English, we use comparative adjectives when we want to compare two objects, people or places; however, we use the superlative adjectives when we want to compare three or more items.

Study these rules!
Here you have some exercises to study and review:
Adjectives: Multiple Choice (Vocabulary)
Opposite Adjectives (Vocabulary)
Adjectives: Classification (Vocabulary) 1
Adjectives: Describing People (Vocabulary)
Adjectives: Crosswords (Vocabulary)
Comparative Adjectives
Comparative Adjectives 2
Comparative Adjectives 3
Comparative Adjectives 4
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative Adjectives 2
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives: Complete the Table
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives 2
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives 3

Study these rules!
Here you have some exercises to study and review:
Adjectives: Multiple Choice (Vocabulary)
Opposite Adjectives (Vocabulary)
Adjectives: Classification (Vocabulary) 1
Adjectives: Describing People (Vocabulary)
Adjectives: Crosswords (Vocabulary)
Comparative Adjectives
Comparative Adjectives 2
Comparative Adjectives 3
Comparative Adjectives 4
Superlative Adjectives
Superlative Adjectives 2
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives: Complete the Table
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives 2
Comparative and Superlative Adjectives 3
Tuesday 21 May 2019
The Periodic Table of Elements
Chemical elements constitute all of the matter around and us.
The term "element" is used for atoms with a given number of protons (regardless of whether or not they chemically bonded, e.g. hydrogen in water) as well as for a pure chemical substance consisting of a single element (e.g. hydrogen gas).
When different elements are chemically combined, with the atoms held together by chemical bonds, they form chemical compounds.
Only a minority of elements (about 32 elements) are found on Earth in native uncombined forms as relatively pure minerals, including copper, silver, gold, carbon (as coal, graphite or diamonds) and sulphur.
However, almost all the other elements are usually found on Earth in chemically combined forms, as chemical compounds and mixtures. For example, atmospheric air is primarily a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, and native solid elements occur in alloys, such as the iron-nickel alloy.
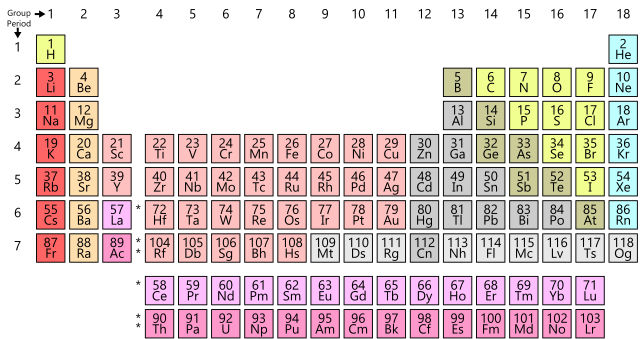
118 elements have been identified, of which the first 94 occur naturally on Earth with the remaining 24 being synthetic elements. They are listed in the Periodic Table.
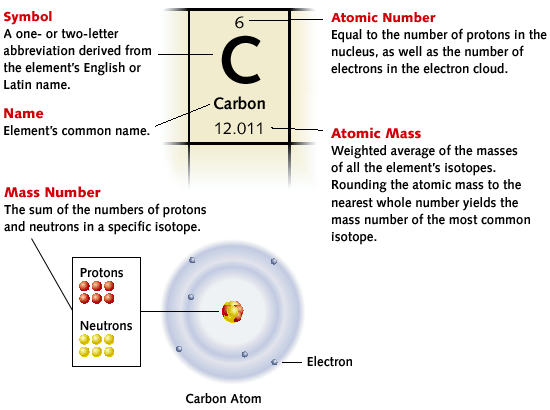
The Periodic Table is a way of listing the elements by the structure of their atoms. This includes how many protons they have as well as how many electrons they have in their outer shell. From left to right and top to bottom, the elements are listed in the order of their atomic number,which is the number of protons in their nucleus as well as the number of electrons in the electron cloud.
Each element has its own name and abbreviation in the periodic table. Some of the abbreviations are easy to remember, like H for hydrogen. Some are a bit difficult like Fe for iron or Au for gold. For gold the "Au" comes from the Latin word for gold: aurum".
It is called "periodic" because elements are lined up in horizontal rows from left to right according to their atomic number, and each row is called period. When they are lined up this way, elements in the columns have similar physical and chemical properties.
Each horizontal row in the table is a period. There are seven (or eight) total periods. The first one is short and only has two elements, hydrogen and helium. The sixth period has 32 elements.
Groups are the columns of the periodic table. There are 18 columns or groups and different groups have different properties.
One example of a group is the noble or inert gases. These elements all line up in the eighteenth or last column of the periodic table. They all have a full outer shell of electrons, making them very stable, so they tend not to react with other elements.
This lining-up and grouping of similar elements helps chemists when working with elements because they can understand and predict how an element might react or behave in a certain situation.
The periodic table was proposed by Russian chemist Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Using the table, Mendeleev was able to accurately predict the properties of many elements before they were actually discovered.
Here you have a song to learn the elements:
If you want to learn more about the elements in the periodic table that constitute all matter around us, have a look at this book:
Thursday 9 May 2019
Present Perfect
Here you have a song with lots of examples of sentences in the Present Perfect:
I Still Haven't Found What I'm Looking For by U2
Here you have some online exercises
to work on this tense:
Etiquetas:
English,
English Tenses,
Grammar,
Review
Wednesday 8 May 2019
Pronunciation of the past simple and past participle: -ed (Regular verbs)

Writing the past simple and past participle of regular verbs in English is quite easy, but...
do you know how to pronounce
<-ed>?
There are some rules:
RULE 1. If the verb ends in the sounds / t / or / d /: <-ed> is pronounced / ɪd /
Examples:
to visit : visited / ɪd / to decide: decided / ɪd /
/ p, k, s, tʃ, ʃ , f /: <-ed> is pronounced / t /
Examples:
to stop: stopped / t / to watch: watched / t /
to walk: walked / t / to finish: finished / t /
to kiss: kissed / t / to laugh: laughed / t /
RULE 3. If the verb ends in a sound which is not in rule 1 o rule 2: <-ed> is pronounced / d /
Examples:
to travel: travelled / d / to play: played / d /
to discover: discovered / d / to live: lived / d /
to open: opened / d / to rob: robbed / d /
Listen to a native speaker pronouncing <-ed>
Here you have a video with some common regular verbs in English in the past simple. Pay attention to pronunciation:
Friday 3 May 2019
A famous artist: Gustav Klimt
Gustav Klimt
 Gustav Klimt, (born July 14, 1862, Vienna, Austria—died February 6, 1918, Vienna), was an Austrian symbolist painter, founder of the school of painting known as the Vienna Sezession. He was one of the pioneers of Austrian Modernism and remained in steady work all his life. In his paintings, he created visual textures by the repetition of small brushtrokes, dot or other shapes. His father was a poor immigrant gold engraver.
Gustav Klimt, (born July 14, 1862, Vienna, Austria—died February 6, 1918, Vienna), was an Austrian symbolist painter, founder of the school of painting known as the Vienna Sezession. He was one of the pioneers of Austrian Modernism and remained in steady work all his life. In his paintings, he created visual textures by the repetition of small brushtrokes, dot or other shapes. His father was a poor immigrant gold engraver.


Beginning in 1894, Klimt’s work grew increasingly controversial. He took a few commissions for public works and did not produce what the patron or public felt was appropriate to be displayed. For example, three of these works showed Philosophy, Medicine, and Jurisprudence as nude women. After this, Klimt stopped taking public commissions.
In 1908 Klimt left the Vienna Secession movement and his art moved into a new phase. It was marked by widespread use of gold leaf. These are the paintings most people are familiar with, including The Kiss and Adele Bloch-Bauer I . In these works he treats the human figure without shadow and heightens the sensuality of skin by surrounding it with areas of flat, highly ornamental, brilliantly composed areas of decoration, in which he applied tiny bits of gold leaf.
Adele Bloch-Bauer I sold in 2006 at auction for more money than any other painting ever had before: $135 million.
Here you have other paintings by Gustav Klimt:
Watch these videos to learn more about this artist:
 Gustav Klimt, (born July 14, 1862, Vienna, Austria—died February 6, 1918, Vienna), was an Austrian symbolist painter, founder of the school of painting known as the Vienna Sezession. He was one of the pioneers of Austrian Modernism and remained in steady work all his life. In his paintings, he created visual textures by the repetition of small brushtrokes, dot or other shapes. His father was a poor immigrant gold engraver.
Gustav Klimt, (born July 14, 1862, Vienna, Austria—died February 6, 1918, Vienna), was an Austrian symbolist painter, founder of the school of painting known as the Vienna Sezession. He was one of the pioneers of Austrian Modernism and remained in steady work all his life. In his paintings, he created visual textures by the repetition of small brushtrokes, dot or other shapes. His father was a poor immigrant gold engraver.
After studying at the Vienna School of Decorative Arts, Klimt in 1883 opened an independent studio specializing in the execution of mural paintings. His early work had a classical style that was typical of late 19th-century academic painting, as can be seen in his murals for the Kunsthistorisches Museum (Museum of Art History) in Vienna.


In 1897 Klimt’s mature style emerged, and he founded the Vienna Sezession, a group of painters who revolted against academic art in favour of a highly decorative style similar to Art Nouveau. During these years, Klimt painted many images of women. He also painted landscapes. like the one shown below, .
 |
| Country Houses on Attersee Lake |
Beginning in 1894, Klimt’s work grew increasingly controversial. He took a few commissions for public works and did not produce what the patron or public felt was appropriate to be displayed. For example, three of these works showed Philosophy, Medicine, and Jurisprudence as nude women. After this, Klimt stopped taking public commissions.
 |
| Philosophy, Medicine, and Jurisprudence |
In 1908 Klimt left the Vienna Secession movement and his art moved into a new phase. It was marked by widespread use of gold leaf. These are the paintings most people are familiar with, including The Kiss and Adele Bloch-Bauer I . In these works he treats the human figure without shadow and heightens the sensuality of skin by surrounding it with areas of flat, highly ornamental, brilliantly composed areas of decoration, in which he applied tiny bits of gold leaf.
 |
| The Kiss |
 |
| Adele Bloch-Bauer I |
Here you have other paintings by Gustav Klimt:
 |
| PortraitMäda Primavesi |
 |
| Portrait of Eugenia Primavesi |
 |
| The Tree of Life |
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)