Hello kids! Some of you seem to be very interested in learning more about the classification of living things, so I have prepared this post for you!
The Classification of Living Things. From Species to Kingdoms:
There are so many living things on Earth that scientists have developed different systems in an attempt to classify them.
Living things are classified depending on how many cells they have, whether their cells are simple (prokarotic cells = they do not have a nucleus) or complex (eukaryotic cells = they have a nucleus), and how they get the nutrients they need to live.
Living things are classified depending on how many cells they have, whether their cells are simple (prokarotic cells = they do not have a nucleus) or complex (eukaryotic cells = they have a nucleus), and how they get the nutrients they need to live.
A SPECIES is a specific type of animals, such as cats, butterflies or apple trees. Their scientific name is made up of two or three words in Latin (Genus + species).
Living things that are closely related are grouped into FAMILIES: domestic cats, lions, tigers and leopards belong to the same family, the felines.
Families are grouped into ORDERS, then CLASSES, then PHYLA and then KINGDOMS.

We can do the same with any living thing. Here you have the classification of an apple tree (Malus domesticus).

Thus, kingdoms are big groups that categorise all living things, from the tiniest bacteria to the biggest whales. Each kingdom has specific defining characteristics that help scientists classify living things.

The five kingdoms are:
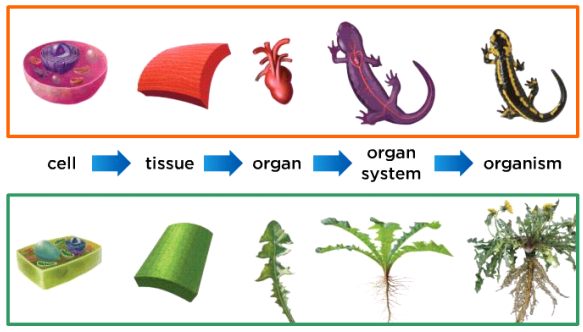
1. Animal kingdom: Animals are multicellular organisms, which means they have more than one type of cell. Their cells are eukaryotic cells. This means that the cells have a nucleus and organelles. Unlike plants, animals get nutrients by eating because they can’t produce energy themselves. Animals also have the ability to move, to respond to their surroundings and to reproduce sexually. The two main groups of animals are Vertebrates and Invertebrates.
1. Animal kingdom: Animals are multicellular organisms, which means they have more than one type of cell. Their cells are eukaryotic cells. This means that the cells have a nucleus and organelles. Unlike plants, animals get nutrients by eating because they can’t produce energy themselves. Animals also have the ability to move, to respond to their surroundings and to reproduce sexually. The two main groups of animals are Vertebrates and Invertebrates.
 |
| VERTEBRATES (Animals that have a backbone) |
 |
| INVERTEBRATES |
2. Plant kingdom: Plants are also multicellular organisms with eukaryotic cells. Unlike animals, plants cannot move. Their cells have a wall cell and chloroplasts. They can make their own food through a process called photosynthesis, in which plants use the light from the Sun. We can classify plants into Non-seed plants (mosses and ferns) and seed plants (gymnosperms and angiosperms)
Non-seed plants:
Seed plants:
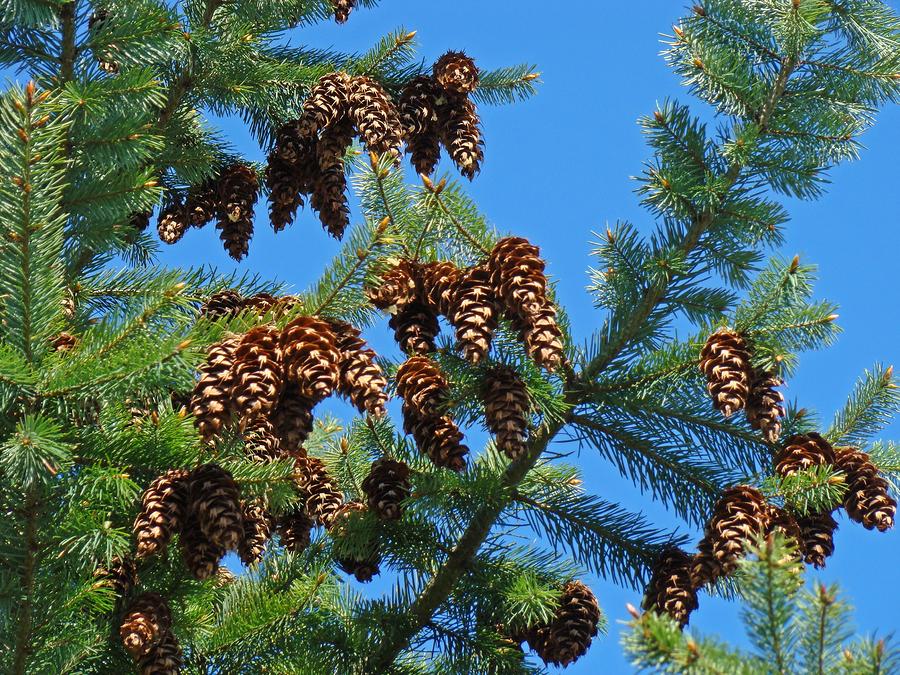
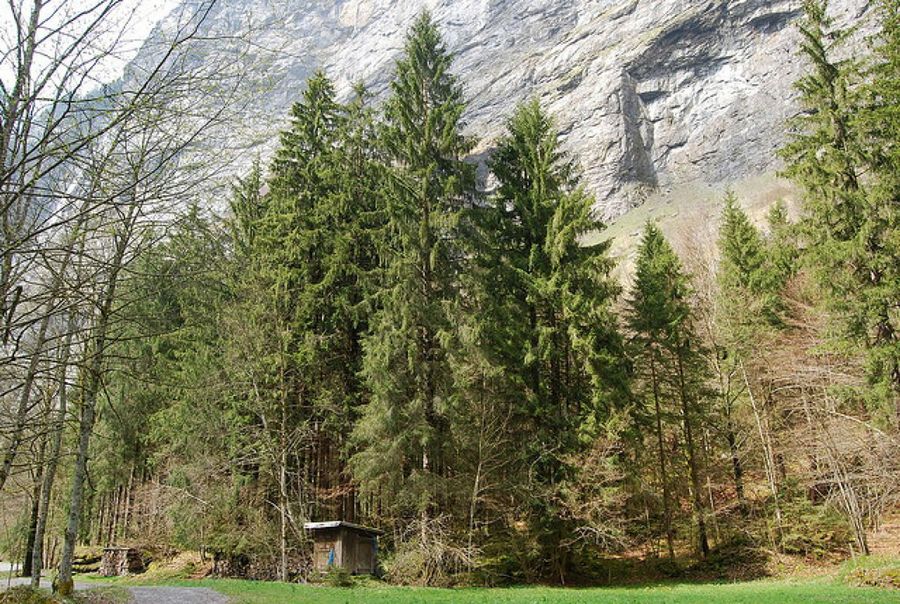
Gymnosperms: they do not produce flowers or fruits, the seeds are grouped in cones.



Angiosperms: they produce flowers and fruits which contain the seeds.



3. Fungi kingdom:

Non-seed plants:
 |
| Mosses |
 |
| Ferns |
Gymnosperms: they do not produce flowers or fruits, the seeds are grouped in cones.



Angiosperms: they produce flowers and fruits which contain the seeds.



Seeds in flower and fruit. Parts of a flower
3. Fungi kingdom:
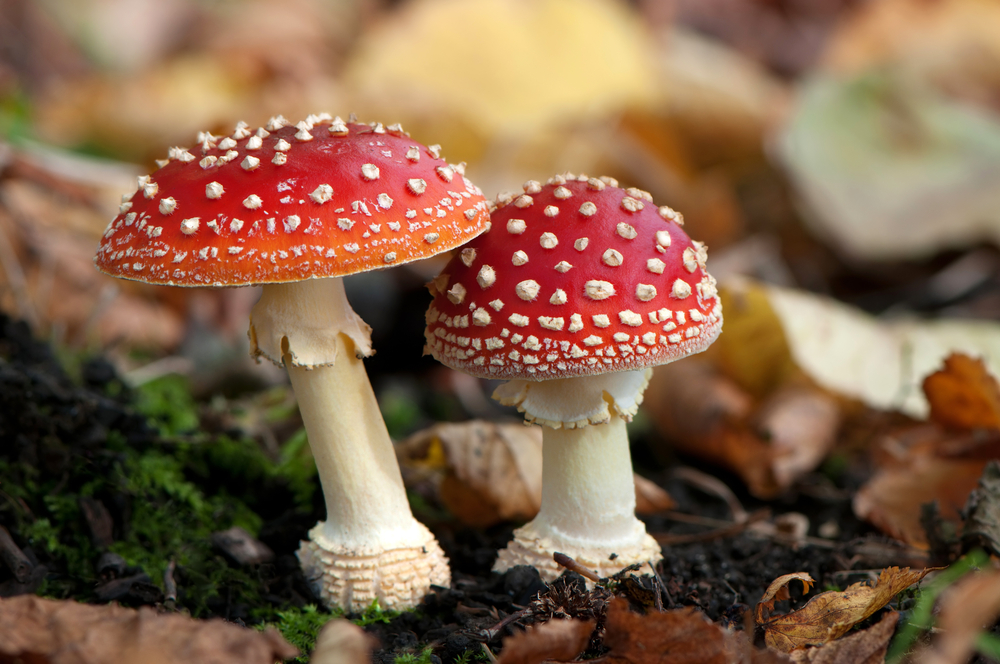
Fungi are multicellular or unicellular organisms with eukaryotic cells. Like plants, fungi have cell walls, but they cannot perform photosynthesis and have to absorb nutrients to get energy. We can find in this kingdom mushrooms, moulds and yeasts.
 |
| Mushrooms (Amanita muscaria) Be careful! It's poisonous |
4. Protist kingdom: most Protists are single-celled organisms , but some are multicellular. They have eukaryotic cells. Some protists eat to get energy like animals and some use photosynthesis like plants. They always live in water. Examples of protists are algae, phytoplankton or protozoa (Paramecium, Euglena, Amoeba).
 |
| Euglena |
 |
| Algae |
 |
| Amoeba |
 |
| Paramecium |
 |
| E. coli |
 |
| Streptococcus pneumoniae |
To understand the classification of living things better, you can watch this video about the classification of human beings.
If you like singing, here you have an amazing song to learn and practise the five kingdoms. It's always easier with music!